Hong Leong Finance Fixed Deposit
- Save and except for the conditions or variations set out herein, all the terms and conditions in relation to Hong Leong Fixed Deposit are applicable hereto and shall remain in full force and effect. Effective date: 3 March 2014 for new customers of HLB. 24 March 2014 for existing customers of HLB as at 3.
- Hong Leong Finance fixed deposit rates (Feb 2021) Hong Leong Finance fixed deposit rate: Interest rate: 0.75% p.a. Deposit amount: Min.
The bonus interest is in additional to attractive rate for deposits that ranges from 0.15% to 0.20% p.a. Depending on amount of deposits. Click here to go to Hong Leong Finance website for more details.
Fixed deposit (sometimes called time deposit) accounts are low-risk investments that earn you interest over a fixed commitment period. You don't need to do anything to earn this interest, just park your money with a bank. Think of it like mold on a piece of bread. Just leave it out in the open and mold will grow — FREE! — on your bread for you. Seriously, though, fixed deposits are great if you have a substantial amount of money lying around and you don’t want to risk investing it. Fixed deposits are an extremely low risk way to grow your money.Best fixed deposit rates in Singapore (Feb 2021)
We've picked the highest fixed deposit rates for SGD in attainable deposit amounts (i.e. $50,000 and below). Note that these promotional rates change monthly and the bank can change the rates anytime.| Bank/financial institution | Min. deposit amount | Tenure | Interest rates |
| DBS | $1,000 | 18 months | 1.3% p.a. |
| Maybank | $1,000 | 36 months | 1% p.a. |
| Hong Leong Finance | $20,000 | 24 months | 0.75% p.a. |
| ICBC | $500 | 12 months | 0.6% p.a. |
| UOB | $20,000 | 10 months | 0.5% p.a. |
| Standard Chartered | $25,000 | 3 months | 0.45% p.a. |
| OCBC | $20,000 | 12 months | 0.4% p.a. |
| RHB | $20,000 | 12 months | 0.4% p.a. |
| CIMB | $1,000 | 3 months | 0.3% p.a. |
| HSBC | $30,000 | 6 months | 0.25% p.a. |
DBS fixed deposit rates (Feb 2021)
| DBS fixed deposit rate | |
| Interest rate | 1.3% p.a. |
| Deposit amount | $1,000 to $19,999 |
| Tenure | 18 months |
Maybank fixed deposit rates (Feb 2021)
| Maybank fixed deposit rate | |
| Interest rate | 1% p.a. |
| Deposit amount | Min. $1,000 |
| Tenure | 36 months |
 Maybank
Maybank  fixed deposit. In February, you can earn 1% p.a. with Maybank's Singapore Dollar Time Deposit. Unfortunately you have to leave it in for 36 months (3 whole years!) to earn that measly 1% p.a. [ms-inline-widget account_type='fixed-deposit' amount='10000' tenure='24' locale='en' country_code='sg' channel='fixed-deposit' product_slug='maybank-singapore-dollar-time-deposit' ]
fixed deposit. In February, you can earn 1% p.a. with Maybank's Singapore Dollar Time Deposit. Unfortunately you have to leave it in for 36 months (3 whole years!) to earn that measly 1% p.a. [ms-inline-widget account_type='fixed-deposit' amount='10000' tenure='24' locale='en' country_code='sg' channel='fixed-deposit' product_slug='maybank-singapore-dollar-time-deposit' ] Hong Leong Finance fixed deposit rates (Feb 2021)
| Hong Leong Finance fixed deposit rate | |
| Interest rate | 0.75% p.a. |
| Deposit amount | Min. $20,000 |
| Tenure | 24 months |
ICBC fixed deposit rates (Feb 2021)
| ICBC fixed deposit rate | |
| Interest rate | 0.6% p.a. |
| Deposit amount | Min. $500 |
| Tenure | 12 months |
UOB fixed deposit rates (Feb 2021)
| UOB fixed deposit rate | |
| Interest rate | 0.5% p.a. |
| Deposit amount | Min. $20,000 |
| Tenure | 10 months |
Standard Chartered fixed deposit rates (Feb 2021)
| Standard Chartered fixed deposit rate | |
| Interest rate | 0.45% p.a. |
| Deposit amount | Min. $25,000 |
| Tenure | 3 months |
OCBC fixed deposit rates (Feb 2021)
| OCBC fixed deposit rate | |
| Interest rate | 0.4% p.a. |
| Deposit amount | Min. $20,000 |
| Tenure | 12 months |
RHB fixed deposit rates (Feb 2021)
| RHB fixed deposit rate | |
| Interest rate | 0.4% p.a. |
| Deposit amount | Min. $20,000 |
| Tenure | 12 months |
What about HSBC and CIMB fixed deposits?
The rest of the banks — CIMB and HSBC — are offering 0.3% or less on their fixed deposits, which is hardly worth your time. In fact, you can get 0.3% p.a. on your savings with no lock-in just by opening a regular CIMB FastSaver account. Of course, banks are notoriously fickle about their interest rates, and all these could easily change next month. For the latest promotional rates, remember to bookmark this page and our MoneySmart fixed deposit comparison page before you commit. Plus, here’s a quick and dirty summary of what you need to know about fixed deposits.Fixed deposit vs savings account — what's the difference?
https://youtu.be/Sq9hjlnEgY0 Once an attractive alternative to that pathetic 0.05% p.a. interest on savings accounts, fixed deposits — like so many ageing Channel 8 starlets — are fading from collective memory. Today, every bank in Singapore is competing for your dollar with high interest savings accounts, which may actually offer better returns. Here are the differences between fixed deposits and savings accounts at a glance:| Fixed deposit | Savings account | |
| Tenure | As low as 3 months, but go for at least 12 months for better rates | None |
| Interest rate | The longer the tenure, the better the interest rate | Usually the same regardless of tenure |
| Amount to deposit | Fixed amount, usually at least $10,000 | Smaller initial deposit and minimum monthly balance ($500 to $3,000) |
| Currency | SGD by default, but some banks offer higher interest rates for foreign currency | SGD by default. There are a few multi-currency accounts, but no difference in interest rate |
| Can you withdraw? | Contrary to popular belief, yes, but you lose the interest | Yes, no impact on interest, but don’t fall below the minimum balance |
| Interest payments | Quarterly or annually | Monthly |
| Risk level | Virtually risk-free, insured up to $75,000 by Singapore Deposit Insurance Corporation (SDIC) |
Fixed deposit vs Singapore Savings Bonds (SSB) — which is better?
Hong Leong Finance Fixed Deposit Rate November 2020
In an earlier article, we compared the Singapore Savings Bonds to fixed deposits. There are a few key distinctions between these virtually risk-free investment vehicles. First, interest rates. Believe it or not, fixed deposit interest rates are actually higher than SSBs. The November issue of SSBs offers a measly 0.23% p.a. interest average return after the first 2 years, which you can easily beat with a well-chosen fixed deposit promotion. Next, entry point. It takes just $500 to invest in Singapore Savings Bonds, which is lower than the $1,000 or more for most fixed deposits. That said, ICBC fixed deposits only require $500 to start. (On the flip side, there's a cap of $200,000 you can put into Singapore Savings Bonds. There's no cap for fixed deposits.) Finally, tenure. Fixed deposits are shorter term investments. After the lock-in period is over, you should shop around again for another place to park your money. With SSBs, however, the interest rate climbs every year, so the longer you keep the money in there (up to a maximum of 10 years) the more you get. At the same time, SSBs have higher liquidity than fixed deposits. You will not be penalised if you withdraw your money at any point. You do have to pay a $2 transaction fee each time you buy or redeem a bond, though. Know anyone who likes to park their cash in fixed deposits? Share this article with them. [ms_related_articles] The post 7 Best Fixed Deposit Rates in Singapore (Feb 2021) — DBS, Maybank & More appeared first on the MoneySmart blog.
$500 to invest in Singapore Savings Bonds, which is lower than the $1,000 or more for most fixed deposits. That said, ICBC fixed deposits only require $500 to start. (On the flip side, there's a cap of $200,000 you can put into Singapore Savings Bonds. There's no cap for fixed deposits.) Finally, tenure. Fixed deposits are shorter term investments. After the lock-in period is over, you should shop around again for another place to park your money. With SSBs, however, the interest rate climbs every year, so the longer you keep the money in there (up to a maximum of 10 years) the more you get. At the same time, SSBs have higher liquidity than fixed deposits. You will not be penalised if you withdraw your money at any point. You do have to pay a $2 transaction fee each time you buy or redeem a bond, though. Know anyone who likes to park their cash in fixed deposits? Share this article with them. [ms_related_articles] The post 7 Best Fixed Deposit Rates in Singapore (Feb 2021) — DBS, Maybank & More appeared first on the MoneySmart blog. MoneySmart.sg helps you maximize your money. Like us on Facebook to keep up to date with our latest news and articles.
| Type | Publicly traded company |
|---|---|
| MYX: 5819 | |
| ISIN | MYL5819OO007 |
| Industry | Financial Services |
| Founded | 1905 |
| Headquarters | Menara Hong Leong, No.6, Jalan Damanlela, Bukit Damansara, 50490, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
| 329 branches | |
Area served | Malaysia Singapore Hong Kong China Vietnam Cambodia United States Australia |
| Quek Leng Chan, Chairman Domenic Fuda, Group Managing Director & CEO | |
| Products | Personal Financial Services Business & Corporate Banking Global Markets Priority Banking Islamic Banking Hong Leong Connect Online Banking Hong Leong Connect Mobile Banking |
| Revenue | MYR 4.039 billion 2014[1] |
| MYR 2.102 billion 2014[1]MYR 1.856 billion 2013[1] | |
| Total assets | MYR 170.4 billion 2014[1] MYR 163.6 billion 2013[1] |
| Parent | Hong Leong Financial Group |
| Website | www.hlb.com.my |
Hong Leong Bank Berhad (MYX: 5819) is a major public listed banking group in Malaysia.
History[edit]
Early beginnings[edit]
Hong Leong Bank began its operations in 1905 in Kuching, Sarawak, under the name of Kwong Lee Mortgage & Remittance Company.[2] The company granted loans against the security of export commodities such as pepper, rubber and other indigenous products. It also provided the services of remitting money of overseas Chinese to their families in the Southeast region of China.
In the initial years, the company went through a difficult period of growth, caught in the middle of a few economic crises. The First World War broke out in 1914 causing panic in the financial circles. A few years after hostilities ended, the post-war Recession of 1920-1921 set in. After the recession, the company opened its branch in Sibu in 1923. Three years later, another branch was opened in Singapore in 1926. The year 1929 saw the start of the Great Depression that lasted until 1933. The Depression caused a sharp fall in the export earnings of commodities and many business concerns, including some banks, were in financial difficulties.
Kwong Lee Mortgage and Remittance Company survived all these setbacks because of its strong cash reserves and its conservative operational policy. Immediately after the Depression, on 26 October 1934, the company was converted into a public company under the name Kwong Lee Bank. Shortly after, the third branch of the Bank was opened in Sarikei in 1937.
The Second World War caused a temporary disruption in the currency and banking system. After the war, the immediate task was one of reconstruction and rehabilitation. In this connection, Kwong Lee Bank played an important role in reviving confidence and business activities by providing financing to enable old businesses to be resumed and new ones to be set up. The aftermath of the war saw the continued expansion of the Bank, and in 1964, Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation of Singapore (OCBC Bank) under the stewardship of Tan Chin Tuan (its then Chairman and Managing Director) acquired a 52% majority stake in Kwong Lee Bank from the Lam family.
In 1973, Kwong Lee Bank opened another branch in Bintangor.
Expansion[edit]
In late 1977, Yang Amat Mulia Tunku Osman Ibni Tunku Temenggong Ahmad, a member of the royal family from the State of Johor, came in as a shareholder of the bank and acquired 30% of its share capital from both OCBC Bank and the Lam family. The period subsequent to this saw a change in the direction of Kwong Lee Bank's expansion. From five banking branch offices in Sarawak (Kuching, Sibu, Sarikei, Serian and Bintangor) and one in Singapore, the bank expanded its operations to Peninsular Malaysia when it opened its first branch in Kuala Lumpur in May 1978 and this was followed by another branch in Johor Bahru during the same month. Over the next four years, a total of six branches were opened in Labis, Segamat, Bintulu, Kota Tinggi, Kota Kinabalu and Kluang and on 1 January 1982, the Head Office was relocated from Kuching to Kuala Lumpur.
Acquisitions[edit]
In May 1982, Kwong Lee Bank Berhad was acquired by the MUI Group, a corporate group controlled by Malaysian business tycoon Tan Sri Dato Khoo Kay Peng. Exiting shareholders include OCBC Bank (which acquired a stake in the bank in 1964) and members of the Lam family (relatives and descendants of the founder Lam Ji Chiew). Kwong Lee Bank Berhad was renamed Malayan United Bank Berhad on 2 February 1983. Subsequently, it was renamed MUI Bank Bhd. Under the MUI banner, the bank grew from 11 branches (including Singapore) to 35 branches.
On 3 January 1994, the Hong Leong Group Malaysia acquired MUI Bank Berhad through Hong Leong Credit Berhad and renamed it as Hong Leong Bank Berhad (HLBB). The acquisition of MUI Bank Berhad by Hong Leong Group Malaysia (which is controlled by Malaysian business tycoon Quek Leng Chan) followed shortly after an aborted takeover attempt by another Malaysian tycoon Tan Sri Dato Vincent Tan Chee Yioun (through his vehicle Berjaya Corporation).
HLBB was listed on the Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange on 17 October 1994 with its total paid-up capital enlarged to RM 470 million. Since then, the growth of the bank has been remarkable.
The consolidation of the banking institution to meet the requirements of Bank Negara Malaysia marks another milestone for Hong Leong Bank Berhad. The completion of the merger of Hong Leong Bank with Wah Tat Bank and Hong Leong Finance with Credit Corporation Malaysia on 1 January 2001 marks the emergence of a larger banking group.
HLBB is a member of the Hong Leong Group. The group has diversified businesses in financial services, manufacturing, property, and infrastructure development.
Acquisition of EON Bank[edit]
On 6 May 2011, Hong Leong Bank announced that it had completed its acquisition on EON Capital Bhd's assets and liabilities, making EON Bank part of Hong Leong Bank Group.
Within close to 8 weeks, the legal vesting was concluded where all assets and liabilities of the former EON Bank was vested into HLB. The merger creates the country’s fourth-largest bank with an asset size of more than RM140 billion, with a total of 329 branches.[3]
Corporate affairs[edit]
Personal banking[edit]
The bank provides banking services and financial products, which include property, auto, personal loans, payment products, share financing, investment, and insurance, as well as deposits and remittance to individuals and small businesses.
Business and corporate banking[edit]
Principal business activities include the provision of banking solutions such as deposit and loan services covering business current account, interest-bearing auto-sweep as well as fixed deposit, and financing options ranging from asset acquisition, working capital, and debt capital market structures, for corporate, commercial and SME client base. HLB also specializes in the provision of transaction banking solutions via cash management, trade financing and services.
Operations[edit]
Principal subsidiaries[edit]
These are HLB's subsidiaries in Asia region.[4]
Malaysia[edit]
- Hong Leong Bank Berhad[4]
- Hong Leong Islamic Bank Berhad
Singapore[edit]
- HL Bank Singapore[5]
Hong Kong[edit]

- Hong Leong Bank Berhad, Hong Kong Branch[6]
Vietnam[edit]
- Hong Leong Bank Vietnam Limited[4]
Cambodia[edit]
- Hong Leong Bank (Cambodia) PLC[4]
China[edit]
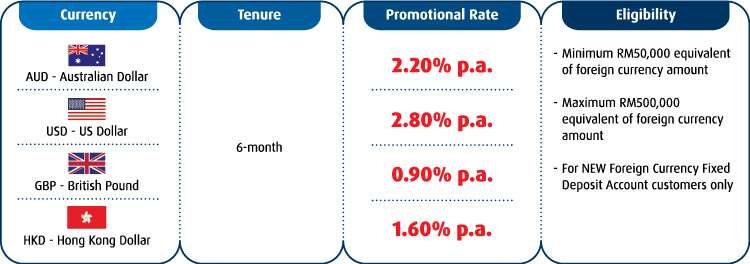
Hong Leong Finance Fixed Deposit Promotion 2021
In March 2010, HLB together with Bank of Chengdu Co., Ltd. (BOCD) formed a joint-venture company named Sichuan Jincheng Consumer Finance Ltd Co (SJCF) to start consumer finance operations in Central and Western China. HLB has a 49% stake in the joint-venture company while BOCD held the rest.[7]
- Bank of Chengdu Co., Ltd - 18% of equity held.[4]
Controversy[edit]
In February 2013, the bank had embarked on a rationalization exercise as part of its continuing efforts to review its business and maintain competitiveness.[8]
As part of the exercise involves transfer non-executive staffs from all over the country to three centralized locations, it created dissatisfactions amongst affected employees. A picket was held at Wisma Hong Leong in November 2013.[9] Alleged wrongful dismissal of the 27 employees for refusing to transfer has been referred to Industrial Court.
References[edit]
- ^ abcde'HLB Annual Report 2014'(PDF). Hong Leong Bank. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- ^'The Hong Leong Bank Story'. Hong Leong Bank. Archived from the original on 9 August 2014. Retrieved 22 July 2015.
- ^EON Bank Group is now part of Hong Leong Bank Group
- ^ abcde'HLB Annual Report 2019'(PDF). hlb.com.my. pp. 219–220. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^'About Us - HL Bank Singapore'. Hong Leong Bank. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^'HL Bank HK'.
- ^'China consumer financing at HLBB's doorstep'. The Edge (Malaysia). Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^'Hong Leong Bank's MD speaks out after union's warning of national action'. The Edge (Malaysia). Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- ^Oei, Melody (10 January 2014). 'Why Malaysians Are Protesting Against Hong Leong Bank'. SAYS. Retrieved 10 January 2014.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hong Leong Bank. |